TRENDING TAGS :
Memories lasts forever; Check out how they form and fade?
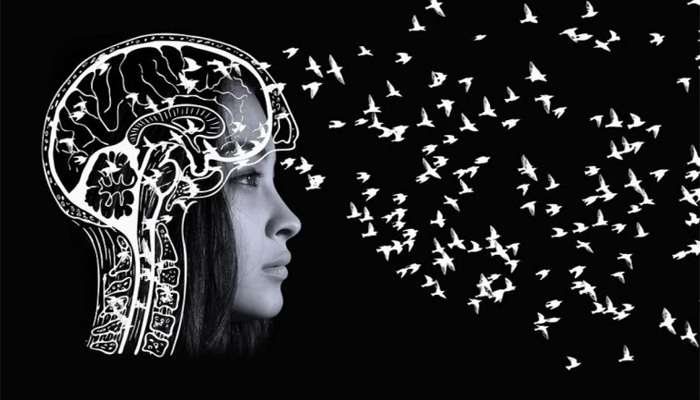
But have you ever wondered how memory is form and fade? Here's a surprising finding from a team of Boston College researchers, who expected recollections would become less accurate, but found people also report declines in the vibrancy and visual qualities of their memories.
Lucknow: Like old photographs, memories also have quality to fade over time. It's a nostalgic feeling whenever we see our old photographs; memories related to that photograph start flashing inside our brain, it's like any short-film starts running and ultimately makes us happy or sad.
But have you ever wondered how memory is form and fade? Here's a surprising finding from a team of Boston College researchers, who expected recollections would become less accurate, but found people also report declines in the vibrancy and visual qualities of their memories.
When people try to remember their past, they remember it with varying degrees of clarity, said Boston College Assistant Professor of Psychology Maureen Ritchey, a cognitive neuroscientist and co-author of the study, published in an online edition of the journal Psychological Science.
Ritchey says that: "Sometimes people remember a lots of details about an event, as if they are reliving the moment as it happened, and Other times it seems like the memory has faded away and the details are fuzzy blurred. Prior memory research has shown that emotionally significant events like a car accident, losing a special person, getting failed in high school are remembered more vividly than everyday events".
ALSO READ:Must read 8 hindi literature classics of Munshi Premchand !!!!
While research, the team asked Ritchey how do memory's visual features changes ? Ritchey told people that mind treat memories like a picture and use a filter to edit a it. A simple analogy is when you post a Instagram photo, You cued to apply filter on it to change brightness or the colour of the picture. Exactly we treat our memories , we apply filters on our memories which some times changes emotional significance of it.
In three experiments,The findings revealed that memories were recollected as less visually vibrant than they were encoded, demonstrating a novel memory-fading effect, the researchers reported. Shape, size, object fades away with the time but experience related to that particular memory remains forever even in our unconscious memory.
Negative emotions subjects experienced when viewing the images increased the likelihood that images would be accurately remembered but did not influence memory fading. Memories like going to a music festival and watching their favorite band, but the intensity of that sensory experience, including the bright stage lights and strength of the bass, will slowly fade.
Cooper the fellow researcher at Boston University said:"We found that memories seem to literally fade: people consistently remembered visual scenes as being less vibrant, We had expected that memories would get less accurate after a delay, but we did not expect that there would be this qualitative shift in the way that they were remembered."
The fading effect happened less for memories that were rated as subjectively stronger. "We were also surprised to find that emotional memories did not influence the amount of fading, only the likelihood with which people remembered the images at all," she added.
ALSO READ:Check out these air purifying plants to fight pollution!!!
Memory serves human beings in many complex ways. It improve our behavior and Give context to our lives. Studies of this psychological phenomenon reveal that memory occurs in stages, which gives us valuable insight into the inner workings of the brain.
The Phenomenon of Memory Brian Becker, Associate professor of neuropsychology at Lesley University, defines memory as “The process in which the mind interprets, stores, and retrieves information." Becker explains, that material is kept in the brain as a mental representation and made retrievable for future use. A number of factors impact the way the brain retrieves a memory — if it’s recalled at all.
The brain has three types of memory processes: sensory register, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
1.Sensory Register: In the sensory register process, the brain obtains information from the environment. This activity is short, lasting at most a few seconds. During sensory register, the brain gathers information passively through visual and auditory cues, known respectively as “iconic” and “echoic” memory.
ALSO READ:The shorter the work week; the lesser will be the carbon emission: Study
Becker gives the examples of a computer screen and a conversation to illustrate how to recognize sensory register. When you look at a computer screen and then look away, but can still see the screen’s image, this is iconic memory at play. Similarly, when you have conversations with others and ask them to repeat themselves, only to understand what they said a moment later, it demonstrates echoic memory.
In the memory-making process, attention is considered a stage between sensory register and short-term memory. Short-term memory formation can begin through giving your attention to the information received through sensory register.
2.Short-Term Memory: According to Becker, short-term memory occurs in two parts: traditionally termed “short-term memory”
and “working memory.” Short-term memory is when the brain stores information temporarily so that it can be repeated, such
as remembering a phone number you see on TV. Working memory refers to the brain storing information for the purpose of
manipulating it, such as remembering a set of numbers while working on a math problem.
When psychologists talk about improving memory, they most commonly focus on working memory because you have the most
control over it and can actively improve it.
3.Long-Term Memory: Many think of long-term memory as a permanent “bank” within the brain. Once a memory arrives there, the mind stores it completely and indefinitely. In truth, this is not the case. Although the long-term memory process allows information to remain in the brain for an extended period, nothing in the brain avoids risk. Information stored in long-term memory can stay in the brain for a short while (a day, a week) or last as long as a lifetime.
When long-term memories form, the hippocampus retrieves information from the working memory and begins to change the brain’s physical neural wiring. These new connections between neurons and synapses stay as long as they remain in use. Psychologists divide long-term memory into two length types: recent and remote.
Long-term memory can also be described by the nature of the memories themselves, You remember implicit memories automatically, like driving a car.You are aware you are actively trying to remember explicit memories. These can further be divided into:
Episodic memories: Contain events that happen to an individual specifically.
Semantic memories: Contain general knowledge.
Decaying theory infers that if a certain memory isn’t repeated, it will eventually deteriorate.
Interference theory infers that new information received by the brain replaces old information (such as the inability to remember an old password after you have created a new one).
Psychologist Daniel Schacter further details the vulnerabilities of the mind in his book The Seven Sins of Memory. These specific failures, which Schacter calls “sins".
ALSO READ:Learn 5 ways to earn money while chilling at your home !!!