TRENDING TAGS :
Understanding India's Response to the JN.1 Variant: Health Ministry Alert
Learn about the current situation, government alerts, and measures being taken to address the rise in COVID-19 cases in certain states.
Understanding India's Response to the JN.1 Variant: Health Ministry Alert
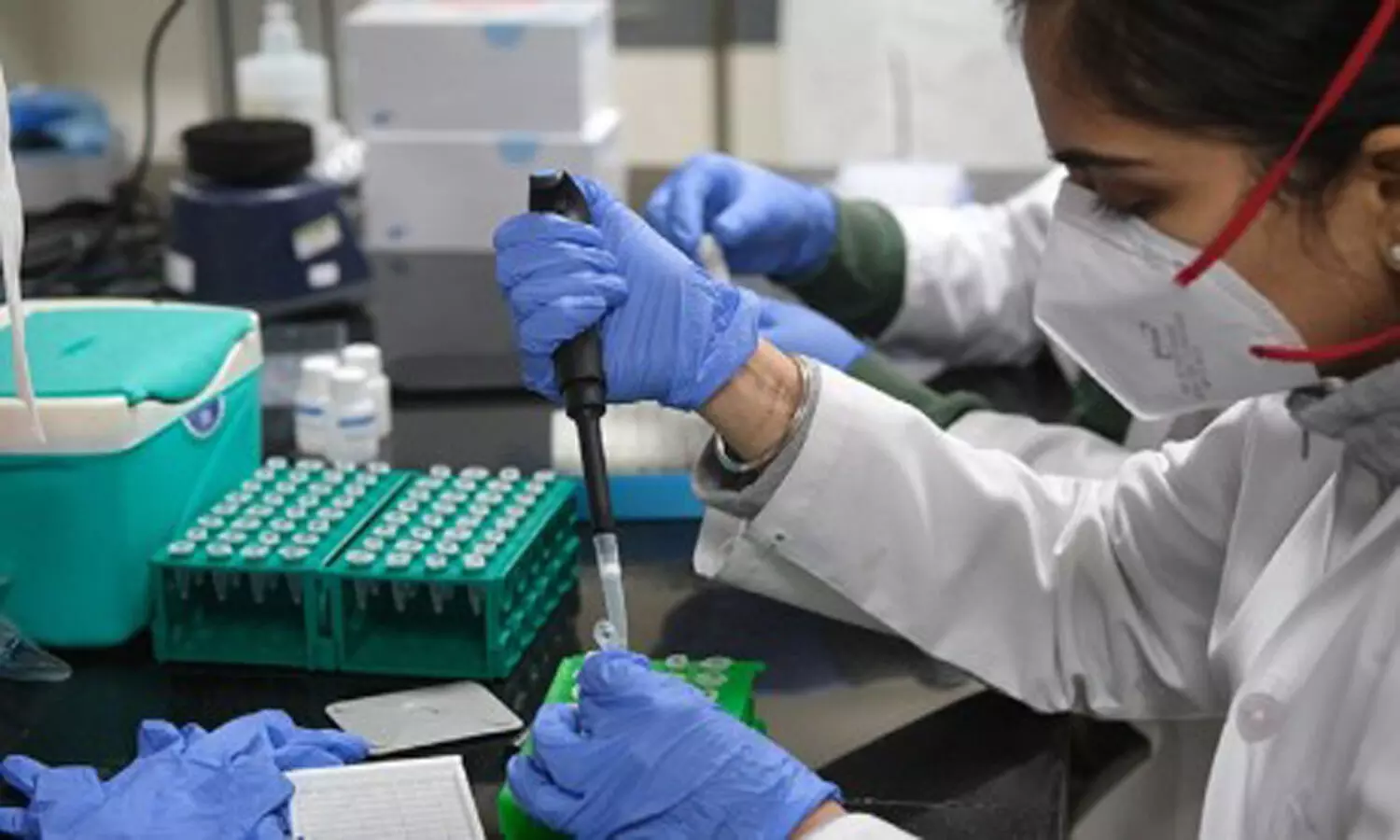
In recent developments, India has witnessed a surge in the daily COVID-19 positivity rate in several states, including Kerala, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, and Karnataka. Responding to this, the Union Health Ministry issued an alert, emphasizing that there is no clustering of cases reported in the new JN.1 variant of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
The Health Ministry acknowledged the rise in the daily positivity rate but reassured the public that the JN.1 variant is currently under intense scientific scrutiny and is not an immediate cause for concern. All reported cases of the JN.1 variant have exhibited mild symptoms, and individuals have successfully recovered without complications.
According to NITI Aayog Member (Health) V.K. Paul, India has detected 21 cases of the JN.1 sub-variant. Notably, approximately 91%-92% of those infected have opted for home-based treatment, indicating the mild nature of the illness associated with this variant. Dr. Paul mentioned that 19 cases have been traced in Goa, with one each in Kerala and Maharashtra. Unfortunately, over the past two weeks, 16 deaths related to COVID-19 were recorded, with many of the deceased having serious comorbidities.
In the backdrop of these developments, the active COVID-19 cases in India have seen a significant rise, though still lower compared to the global scenario. Ministry data highlights that 92.8% of the cases were home-isolated, suggesting mild illness.
The Union Health Minister, Mansukh Mandaviya, stated that there has been no observed increase in hospitalization rates due to COVID-19. He emphasized that cases requiring hospitalization are primarily due to other medical conditions, with COVID-19 being an incidental finding.
The Health Ministry's alert closely follows the World Health Organization's (WHO) classification of the JN.1 variant as a separate Variant of Interest (VOI) from the parent lineage BA.2.86. Despite the rapid spread, the additional global public health risk posed by JN.1 is currently evaluated as low. The WHO assured that current vaccines continue to protect against severe disease and death from JN.1 and other circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2.
In response to the evolving situation, the Health Ministry directed the strengthening of the surveillance system for whole genome sequencing of positive case samples. This effort aims to track variants through the Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG) network, enabling timely detection of newer variants circulating in the country.
States have been urged to ramp up testing, referring large numbers of samples to INSACOG Genome Sequencing Laboratories daily. This measure is crucial for sequencing and tracking new variants, if any.
Union Health Minister Mandaviya emphasized the need for states to remain alert, increase surveillance, and ensure adequate stocks of medicines, oxygen cylinders, concentrators, ventilators, and vaccines. States are directed to undertake mock drills regularly to assess the functionality of essential medical equipment.
As India faces a surge in COVID-19 cases, especially during the upcoming festive season, the Health Ministry calls for preparedness for new and emerging strains of the virus. The ministry urges states to monitor emerging evidence of COVID-19 cases, symptoms, and severity to plan appropriate public health responses.
In conclusion, India's response to the JN.1 variant underscores the importance of vigilance, surveillance, and proactive measures to mitigate the impact of COVID-19. The Health Ministry's alert serves as a reminder that the pandemic is not over, and collective efforts are essential to manage and overcome new challenges posed by emerging variants.