TRENDING TAGS :
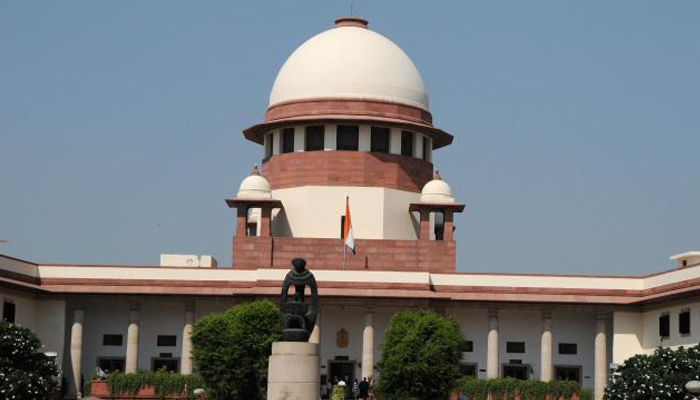
Implement Lokpal without LOP, says Supreme Court to Centre
The bench said, "Attempts at achieving better results in the working of any statute is a perpetual and ongoing exercise dictated by the experiences gained on the working of the act. Such attempts cannot halt the operation and execution of the law which the Executive in its wisdom has already given
New Delhi: The Supreme Court has observed that there is no justification to keep the enforcement of the Lokpal Act under suspension, as the compilation of proposals in the current version of Lokpal Act was eminently workable piece of legislation.
Thus, giving a way for more transparency in governance, the SC has dismissed the Centre's contention and gave Lokpal Committee the permission to go ahead with appointing the rest of the members, including an eminent jurist, even if there was no Leader of Opposition (LOP).
The apex court released a statement saying, “If, at present, the LOP is not available, surely, the chairperson and the other two members of the Selection Committee, namely the Speaker of the Lok Sabha and the Chief Justice of India or his nominee, may proceed to appoint an eminent jurist as a Member of the Selection Committee under Section 4(1)(e) of the Act."
The decision was taken by the bench comprising Justices Ranjan Gogoi and Navin Sinha, who further found that Acts undergo amendments all the time and stated that while this is a continuous process, we cannot let the operation and execution of the law be halted.
Also Read: I have no relationship with Arvind Kejriwal now: Anna Hazare
The bench said, "Attempts at achieving better results in the working of any statute is a perpetual and ongoing exercise dictated by the experiences gained on the working of the act. Such attempts cannot halt the operation and execution of the law which the Executive in its wisdom has already given effect to and has brought into force by resorting to the provisions of Section 1(4) of the Act."
The case:
- The Lokpal Act was passed by the parliament in December 2013, and notified the following month.
- It was, however, inactive since there was no Leader of Opposition, as understood by the parliament.
- The Centre kept on claiming that since Congress, the single largest opposition party, did not have the requisite number of seats in the parliament and hence, did not have a recognized LOP.
- Centre has claimed that the act could not be implemented until thjere is a LOP.
- Mallikarjun Kharge is the leader of the main Opposition party, but the government did not give him the status of Leader of Opposition.
- Unless the proposed amendment is not made, the committee cannot be formed, stated the Centre before the court.
You May also Read: Sahara chief parole extended following undertaking given to SC
The Lokpal Bill:
- The Jan Lokpal Bill, also known as the Citizen's Ombudsman Bill, is an anti-corruption bill that was drafted by civil society activists in India seeking the appointment of a Jan Lokpal.
- The Jan Lokpal will be an independent body to investigate corruption cases, complete them within a year and envisage the subsequent trial to be complete in the following year.
- Leader of Opposition in the Jan Lokpal will be the constitutional post and he along with the Chief Justice of India, the Prime Minister and the Speaker and the LoP would select the committee that would investigate allegations of corruption against public servants and officials.
- Lokpal at the Centre and Lokayukta in each state will be set up.
- It would be independent to prevent any influence from ministers or bureaucrats.
- The loss caused to the exchequer would be recovered from the accused at the time of conviction.
- The Lokpal Bill is expected to make government officials responsible towards their public duties.
- If the government official failed to dispense his duties, he/she would be liable to a financial penalty which would be given to the complainant as compensation.