TRENDING TAGS :
Indian Banking Industry Analysis : Report By IBEF
The Indian banking system consists of 20 public sector banks, 22 private sector banks, 44 foreign banks, 44 regional rural banks, 1,542 urban cooperative banks and 94,384 rural cooperative banks, in addition to cooperative credit institutions. As on March 31, 2019, the total number of ATMs in India increased to 2,21,703 and is further expected to increase to 407,000 by 2021. As of 2017, 80 per cent of the adult population has bank accounts. As on March 31, 2019 the number of debit and credit cards issued were 925 million and 47 million, respectively.
As of Q3 FY19 (between April–September 2018) total credit extended by commercial banks surged to Rs 90.81 lakh crore (US$ 1,299.39 billion) and deposits grew to Rs 120 lakh crore (US$ 1,866.22 billion). Assets of public sector banks stood at Rs 108.82 crore (US$ 1,557.04 billion) in FY18. As per Union Budget 2019-2020, Provision coverage ratio of banks reached highest in 7 years. As per RBI, as of October 25, 2019, India recorded foreign exchange reserves of approximately US$ 442.58 billion.
Indian banks are increasingly focusing on adopting integrated approach to risk management. The NPAs (Non-Performing Assets) of commercial banks has recorded a recovery of Rs 400,000 crore (US$ 57.23 billion) in FY2019, which is highest in last four years. Banks have already embraced the international banking supervision accord of Basel II, and majority of the banks already meet capital requirements of Basel III, which has a deadline of March 31, 2019.As per Union Budget 2019-20, investment-driven growth requires access to low cost capital which an requires investments of Rs 20 lakh crore (US$ 286.16 billion) every year.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has decided to set up Public Credit Registry (PCR) an extensive database of credit information which is accessible to all stakeholders. The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Ordinance, 2017 Bill has been passed and is expected to strengthen the banking sector. In June 2019, RBI sets average base rate of 9.18 per cent for non-banking financial companies and micro finance institutions borrowers for quarter beginning of July.
The total equity funding of microfinance sector grew at the rate of 42 year-on-year to Rs 14,206 crore (US$ 2.03 billion) in 2018-19.
Deposits under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) stood at Rs 1.06 lakh crore (US$ 15.17 billion) with 37.34 crore accounts registered. In May 2018, the Government of India provided Rs 6 lakh crore (US$ 93.1 billion) loans to 120 million beneficiaries under Mudra scheme. As of November 2019, the total number of subscribers was 19 million under Atal Pension Yojna.
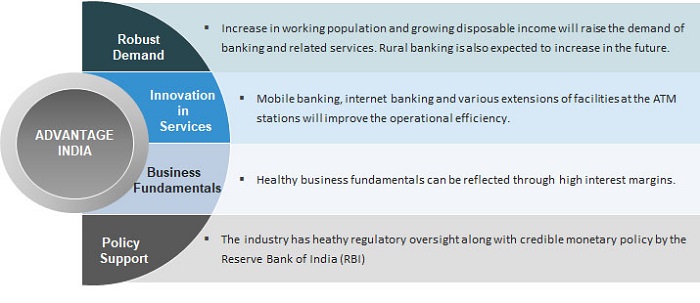
Rising incomes are expected to enhance the need for banking services in rural areas and therefore drive the growth of the sector. As of September 2018, Department of Financial Services (DFS), Ministry of Finance and National Informatics Centre (NIC) launched Jan Dhan Darshak as a part of financial inclusion initiative. It is a mobile app to help people locate financial services in India.
The digital payments revolution will trigger massive changes in the way credit is disbursed in India. Debit cards have radically replaced credit cards as the preferred payment mode in India, after demonetisation. Transactions through Unified Payments Interface (UPI) stood at 1.15 billion in October 2019 worth Rs 1.91 lakh crore (US$ 27.33 billion).
As per Union Budget 2019-20, the government has proposed fully automated GST refund module and an electronic invoice system that will eliminate the need for a separate e-way bill.
Courtesy: IBEF.